Compatibility Files
Windows Vista introduced several new security-related concepts - the most
well known of these is UAC. One of the features of the new
security system is the ability for file operations in certain protected
locations to be automatically redirected to a different, non-privileged
location. This system kicks into action whenever an older program that hasn't
been updated for UAC tries to create or write to files in locations like the
Windows directory. The file-system silently diverts the application to
a different location - this means the old application doesn't break, but
security is not compromised by allowing non-privileged applications write
permission in important system folders.
Files that have been written to disk as a result of this system are known as
compatibility files. Opus gives you the ability to manage compatibility
files in two ways:
- Whenever you are in a protect location that has a compatibility folder,
the Compatibility Files button (
 ) will appear on the File Display Toolbar.
Clicking this button will instantly move you to the compatibility folder for
the current location. Click the button again to return to the original
folder.
) will appear on the File Display Toolbar.
Clicking this button will instantly move you to the compatibility folder for
the current location. Click the button again to return to the original
folder.

For example, say you are in the C:\Windows
directory. As this is a protected location, the Compatibility
Files button may appear on the toolbar (if it doesn't appear it means
there aren't any compatibility files for the current location).

Clicking the button would take you to your
personal VirtualStore folder for the Windows directory.
- You can turn on the Show compatibility files option on
the Folder Options
dialog's Options tab. If this option is on, any
compatibility files for the current folder are automatically included in a
merged view with the current folder. You can also set this option as a global
default with the Display Compatibility Files where possible
option on the Folders / Folder Display
Preferences page.
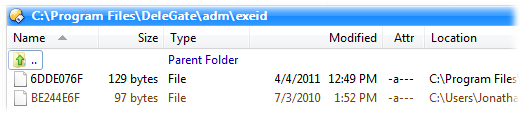
Files from the alternate location are
displayed in a different color to regular files and folders - you can
configure this color from the Display / Colors and
Fonts Preferences page. For example, the screenshot above shows
that the program Delegate has attempted to write a file to the
C:\Program Files folder, and this was silently diverted to the
compatibility store. If you add the Location column to the
display it also indicates which files are compatibility files.
 ) will appear on the File Display Toolbar.
Clicking this button will instantly move you to the compatibility folder for
the current location. Click the button again to return to the original
folder.
) will appear on the File Display Toolbar.
Clicking this button will instantly move you to the compatibility folder for
the current location. Click the button again to return to the original
folder.

